源源刨析
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-from rest_framework.views import APIViewfrom rest_framework.response import Responseclass TestView(APIView): def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs): # self.dispatch print(request.user) print(request.auth) return Response('GET请求,响应内容') def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return Response('POST请求,响应内容') def put(self, request, *args, **kwargs): return Response('PUT请求,响应内容') 在上面刚开始请求进来,先不执行自己写的方法,如:(get、post、put),它会先执行dispach方法,如果没有,就回去它的父类去找。
执行它父类的dispach

Django rest framework流程:
原来用CBV的时候它继承from django.views import View中的views方法,在写get,post方法 如:class HostView(view)
如果有Django rest Framework它就不用继承from django.views import View中的views方法,而是:
先导入:from rest_framework.views import APIView它就会继承APIView,不在继承django的views如:class AuthView(APIView):
from rest_framework.views import APIView 先导入APIView
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
class AuthView(APIView): 继承APIView authentication_classes=[] def get(self,request):return Response('....’) 而在class AuthView(APIView)中它继承的APIView,而APIView它有继承了view,view它在rest_framework view 中如下图:
点击view它就会到django的view中,而这个view是以前CBV 中的那个view,如下图:
继承的这个类比原来django的这个类跟多了点功能,而它的本质还是和原来的一样先执行dispatch,自己有就执行自己的,没有就执行父类的,父类如果没有它就执行原来的dispatch 。
虽然以前它的本质一样但是现在却发生变化,现在它的request是rest_framework中的request,而原来的request是django中的request,如:
class HostView(APIView): def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs): # 原来request对象,django.core.handlers.wsgi.WSGIRequest # 现在的request对象,rest_framework.request.Request\ self.dispatch 请求进来先执行dispatch print(request.user) print(request.auth) return Response('主机列表') 1、请求进来先执行dispatch,而dispatch它在APIView中,dispatch在它里面有,先执行它自己,如果把它先删除它就会先执行默认的那个就是django提供,如下图:
请求进来它源码就是从现在开始如下:
源码的第一步:
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs): 请求进来先执行dispatch """ `.dispatch()` is pretty much the same as Django's regular dispatch, but with extra hooks for startup, finalize, and exception handling. """ self.args = args dispatch先把参数获取到 self.kwargs = kwargs #1、对request进行加工 ''' 源码进来的第一步 1、request对象中(它比原来的类中封装了好多):
request, parsers=self.get_parsers(), authenticators=self.get_authenticators(), 这里面放的是两个列的对象 negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(), parser_context=parser_context
''' request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs) 在这执行了这个方法,它返回了request self.request = request self.headers = self.default_response_headers # deprecate? try: 第二步:2 self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs) # Get the appropriate handler method if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names: #在这执行反射 handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(), self.http_method_not_allowed) else: #反射后拿到结果 handler = self.http_method_not_allowed第三步:3.执行get/post/delete/put等函数 response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs) 返回结果 except Exception as exc: response = self.handle_exception(exc)第四步:4、对返回结果再次加工 self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs) return self.response
在执行 request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)时,先去自己写的找,没有再去父类找,上面是自己没有就去父类找,如下图:
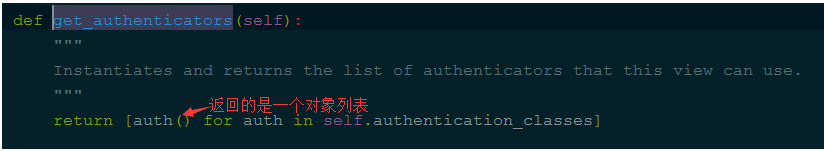
上面没有就去拿它的静态字段,如下图:
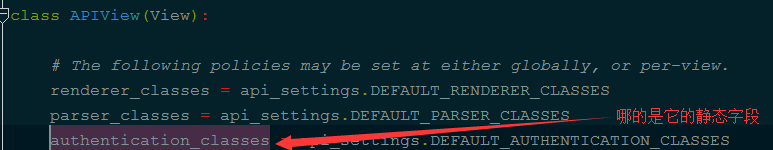
在这上面执行时request被加工,如下图:
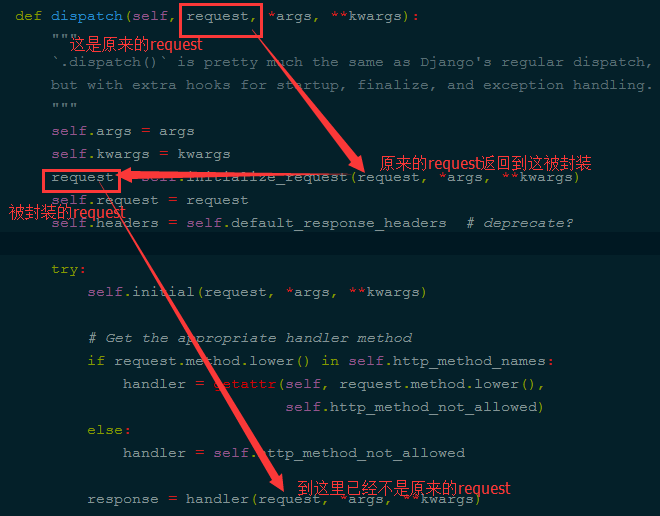
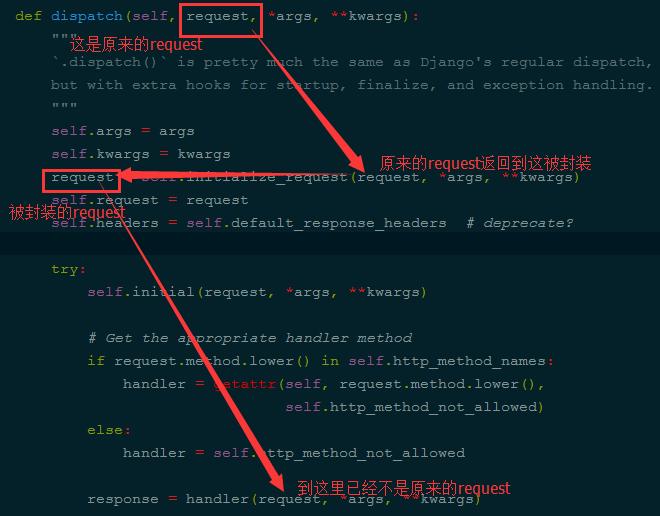
源码执行的第二步:
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs): """ Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler. """ self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs) # Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request) request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg # Determine the API version, if versioning is in use. 2.1处理版本信息 version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs) request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme # Ensure that the incoming request is permitted 2.2认证授权 self.perform_authentication(request) 2.3权限验证 self.check_permissions(request) 2.4请求用户限制访问频率 self.check_throttles(request)
执行源码第二步中的2.2认证授权:
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs): """ Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler. """ self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs) # Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request) request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg # Determine the API version, if versioning is in use. version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs) request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme # Ensure that the incoming request is permitted self.perform_authentication(request) 执行这一步,点击就去如下图: self.check_permissions(request) self.check_throttles(request)
还是先找自己的,没有才执行以下的: def perform_authentication(self, request): """ Perform authentication on the incoming request. Note that if you override this and simply 'pass', then authentication will instead be performed lazily, the first time either `request.user` or `request.auth` is accessed. """ request.user 在这里request是传过来的request,不是原来的request
尽接着下一步它就会找user,如下图:
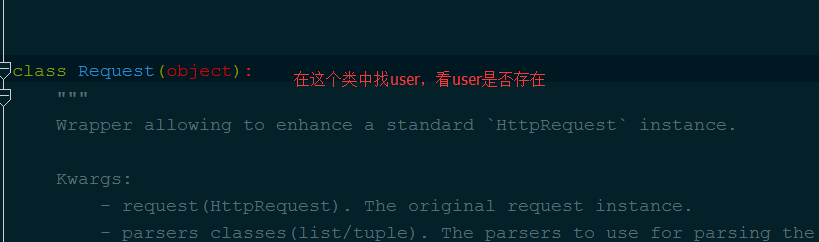
找到user : def user(self): """ Returns the user associated with the current request, as authenticated by the authentication classes provided to the request. """ if not hasattr(self, '_user'): 如果没有user self._authenticate() 就会这行self._authenticate()这个方法,在找到这个方法
return self._user
def _authenticate(self): """ Attempt to authenticate the request using each authentication instance in turn. """ 循环对象列表 for authenticator in self.authenticators: 在这里authenticators是那个对象列表,它循环这个对象列表 try: 执行每一个对象authenticate方法 user_auth_tuple = authenticator.authenticate(self) 在这里它返回了两个值 except exceptions.APIException: 没有验证成功就会报错 self._not_authenticated() raise if user_auth_tuple is not None: self._authenticator = authenticator self.user, self.auth = user_auth_tuple 这里self.auth,self.user,就会有值,验证成功就会通过 return self._not_authenticated()
